Hexanole
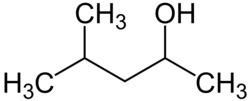
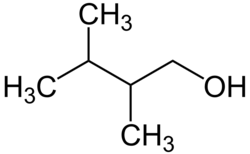
Die Hexanole bilden in der Chemie eine Stoffgruppe von aliphatischen, gesättigten, einfachen Alkoholen (Alkanolen) mit 6 Kohlenstoffatomen und damit der Summenformel C6H13OH. Es gibt 17 Strukturisomere. Das Isomerengemisch besitzt die CAS-Nummer 25917-35-5.
Strukturformel Typ IUPAC Name Siedepunkt (°C) Primär 1-Hexanol 158 
Sekundär 2-Hexanol 136 Sekundär 3-Hexanol 135 Primär 2-Methyl-1-pentanol 147 Primär 3-Methyl-1-pentanol 152 Primär 4-Methyl-1-pentanol 151 Tertiär 2-Methyl-2-pentanol 121 Sekundär 3-Methyl-2-pentanol 134 Sekundär 4-Methyl-2-pentanol 131 Sekundär 2-Methyl-3-pentanol 126 Tertiär 3-Methyl-3-pentanol 122 Primär 2,2-Dimethyl-1-butanol 137 Primär 2,3-Dimethyl-1-butanol 145 Primär 3,3-Dimethyl-1-butanol 143 Tertiär 2,3-Dimethyl-2-butanol 119 Sekundär 3,3-Dimethyl-2-butanol 120 Primär 2-Ethyl-1-butanol 146